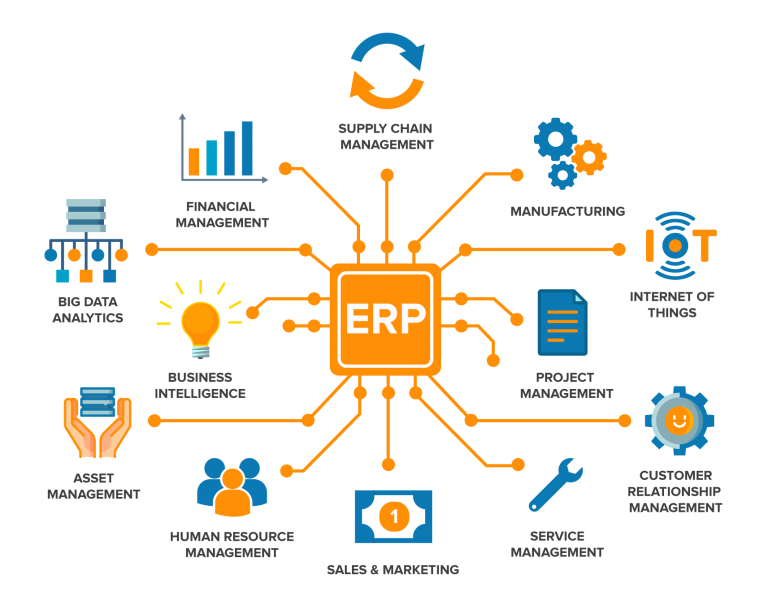
Introduction of ERP
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) is a familiar term for businesses in this day and age, whether for big, medium, or small businesses. This is because no business operates independently. Stakeholders from different departments work together to ensure the success of the business. That’s where an ERP solution comes into play, offering an integrated process to connect the data flow seamlessly, making it easier for businesses regardless of size and regional operations to access important information for decision making.
Enterprise resource planning (ERP) is defined as the ability to deliver an integrated suite of business applications. ERP tools share a common process and data model, covering broad and deep operational end-to-end processes, such as those found in finance, HR, distribution, manufacturing, service and the supply chain. – Gartner
A Brief History of ERP
ERP has its roots in material requirements planning (MRP) and materials requirements planning II (MRP II), with the former being used for production planning, scheduling, and inventory control system, and the latter being used to address operational planning, financial planning, and essentially the planning of all resources of a manufacturing company. Since the 1990s, ERP solution has evolved to represent the application integration beyond manufacturing, and many businesses have deemed it necessary for their business growth.
Benefits of ERP for Your Business
#1 Greater Transparency & Better Flow of Information among Teams
A typical organization is made up of functional teams such as finance, human resources, operations, sales & marketing, logistics & inventory. For a small business that just launched, teams are lean (i.e. each staff takes on multiple hats) and information can be easily shared between parties by email, google drive or excel sheet. Once the business starts to expand into multiple headcounts per department, the manual way of updating an excel sheet or google drive would no longer be feasible. Having an ERP solution that integrates the core functional departments such as finance, human resources, and sales would create a centralized system for functional teams to view and share important information easily.
#2 Customizable and Flexible
Choose from cloud-based ERP to on-premise ERP solution; integrate your new system with existing software; add additional licenses so that more stakeholders can view important data. ERP systems with multiple modes of deployment such as DevOps, CaaS, micro-service, and Open API, can quickly adapt to the different needs a business has to create a uniform experience.
#3 Enables Data-driven Decision Making
For a business entering the growth or maturity life cycle, data is important for decision-makers to make effective and strategic calls for the business. Data-based decision management helps leaders to mine data and refine strategies for the benefit of the business. Being analytical also allows the management team to view and analyze historical data that can predict business behavior and prepare for up/downtrends in the business.
#4 Reduce Operational Costs
ERP solution helps to automate and optimize operations, so more work can be done by lesser people. Employees that were doing manual work before, can be retrained and reskilled to perform other tasks. Each department will have access to a central database, which effectively lowers the costs of setting up & maintaining multiple data centers.
#5 Supports Mobile Working
Digitizing your business and operations with a unified system ensures that employees can work at their place of convenience, and operations can carry on as per usual. Month-end closing can be done on time and shared with teams across the region.
Conclusion
Every business owner dreams of bringing the company to greater heights. To do so, it is important to set the fundamentals of the business right, so business leaders can focus on what’s important without stumbling into roadblocks that would delay the process.
Sources: Wikipedia – ERP, Wikipedia – MRP
